US Black People More Likely To Die From COVID-19: Study
especiales
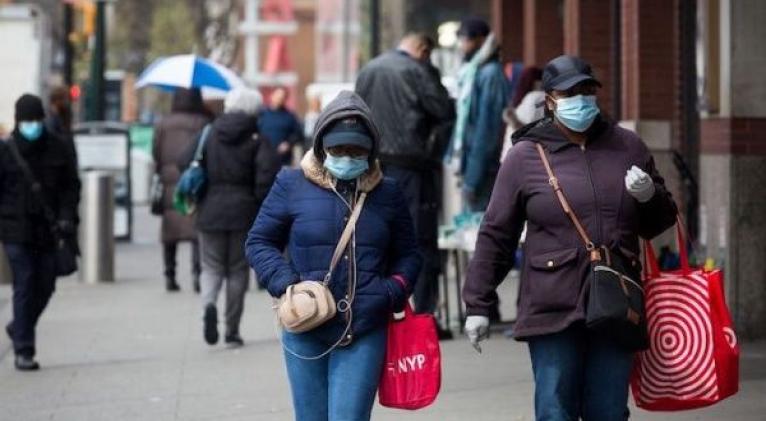

Early data from U.S. states shows black people are more likely to die from COVID-19, highlighting longstanding disparities in health and inequalities in access to medical care, experts said Monday.
In Illinois, black people make up about 30 percent of the state’s cases and about 40 percent of its coronavirus-related deaths, according to statistics provided by the state’s public health agency. However, they just make up 14.6 percent of the state’s population.
In Michigan, black people account for 40 percent of the state’s reported deaths, according to data released by the state, but its population is only 14 percent.
Many U.S. states, including hardest-hit New York, have not released demographic data showing the virus’ toll on different racial groups.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention also has not publicly reported data on the race and ethnicities of patients tested for COVID-19, the sometimes deadly respiratory illness caused by the new coronavirus.
“Because we don’t have broad access to testing, we don’t actually know how many people are infected in the U.S.,” said Dr. Jeffrey Levi, a professor of public health at The George Washington University. “We only have accurate data on who is actually getting hospitalized.”
In a letter sent late last month, a group of Democratic lawmakers including Sen. Elizabeth Warren and Sen. Kamala Harris urged Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar to ensure such data is collected and published.
The World Health Organization has said people with pre-existing conditions like asthma and other chronic lung disorders, diabetes and heart disease appear to develop serious illness more often than others.
That makes the virus particularly dangerous for black people, who because of environmental and economic factors have higher rates of those illnesses, said Dr. Summer Johnson McGee, dean of the School of Health Sciences at the University of New Haven.
McGee said she was not surprised the U.S. black population is experiencing a worse outcome during the pandemic. Racism has led to a lack of investment in black communities and worse health care for the population in general, McGee said.
“A pandemic just magnifies the disparities in healthcare that many communities of color face,” she said.
Confirmed U.S. coronavirus cases neared 350,000, with more than 10,000 deaths, on Monday, according to a Reuters tally.













Add new comment