Floods of Ukrainian Refugees Seek New Life in Russia
especiales
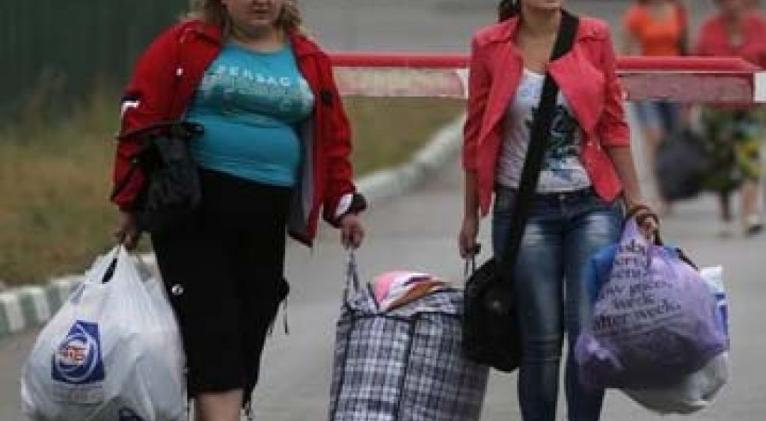

The two-day, 250-km (150-mile) car journey from the city of Slaviansk to the quiet provincial city of Belgorod in June was the most hazardous of their life, taking them across territory hit by fighting and through six checkpoints.
"My son may never pick up a toy gun again. The children had guns pointed at them at checkpoints. They were pale with fear," said Svetlana Divenko, a 28-year-old housewife.
But like many other Russian-speaking east Ukrainians, discontent with the economic situation at home and resentful of Ukraine's Western-looking leaders, the Divenko family headed to Russia not only to seek safety but in search of a better life.
The United Nations says more than 1 million people have been displaced by the conflict. A Russian immigration official last week also put the number of Ukrainian refugees now in Russia at 1 million although Ukrainian officials say the number is vastly exaggerated by Moscow for political reasons.
Russia wants to use the refugee crisis to show its humane side to Western nations critical of its conduct over Ukraine, where pro-Russian separatists in the Russian-speaking east rose up against government forces in mid-April.
The refugees have been greeted warmly by their fellow Russian Orthodox Slavs, offered shelter and some given jobs.
Many were initially housed in tents in refugee camps near the border. Some found temporary homes in the apartments of sympathetic Russians and others have made their way to areas long distances from the border, including cities close to Moscow and in the North Caucasus and far east.
President Vladimir Putin often refers to Ukrainians as "brothers" and said before the conflict that Ukrainians and Russians were one people. Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev says the refugees should be provided for, given jobs and educated.
Some now dream of staying for good, even though a fragile ceasefire has been in force in east Ukraine since Sept. 5.
"We don't see any future in Slaviansk," Divenko said, glad to be out of the firing line in a conflict that has killed more than 3,500 people and for now in a country with a much bigger economy.
Securing Russian citizenship could be beyond most refugees as it usually takes many years and this would also not augur well for eastern Ukraine's already struggling economy. But migrant workers are in general embraced in Russia because of a decline in the birth rate since the Soviet Union collapsed, so the Ukrainians will not give up hope easily.
"CITY OF KINDNESS"
In Belgorod, many refugees are housed in small apartments.
"Belgorod is a city of kindness and prosperity," declare banners hanging across the city of 400,000, some 40 km from the border with Ukraine and 700 km south of the capital, Moscow.
Belgorod for the most part lives up to the image although there are pockets of resentment towards the refugees who have been arriving for months and the benefits they receive.
"Life is hard here as it is and now we have you on top of all that!" an elderly woman shouted at a Ukrainian man sifting through old vegetables on sale at the city's market.
The Russian government says it spends 800 roubles (20 dollars) a day on each Ukrainian refugee, covering the cost of food and accommodation. Some Russian firms are also helping by making donations - oil producer Lukoil said this week it would buy goods for refugees worth 3.5 million roubles.
City authorities say more than 60,000 displaced Ukrainians have come to the Belgorod region alone.
Their arrival is for most residents one of the few physical signs of the conflict nearby. Other reminders are occasional sightings of military ambulances or trains carrying military equipment and armoured vehicles on the outskirts of the city, though Russia denies backing the rebels with troops or weapons.
Many of the refugees congregate around the local immigration office in Belgorod which is patrolled by the police.
After a three-month wait, the Divenkos obtained a coveted one-year temporary asylum permit from the office, allowing them the right to free meals, accommodation at a designated facility and medical assistance.
The four of them now live in a studio apartment that is in need of renovation. The owner has warned them to be ready to go at short notice because the apartment is up for sale.
Sergei Divenko, a mechanical engineer, has a job as a car mechanic and makes up to 20,000 roubles a month. The rent eats up 12,000 roubles.
"We used to indulge our kids back home, but here, of course, we are living hand-to-mouth. Free meals help, the locals bring us clothes - we arrived with just one bag," his wife said.
The Divenkos used to earn about the same in Ukraine but it stretched further. Even so, they are in no rush to go home.
LOOKING FOR WORK
Standing in line at the city's immigration office, a woman who gave her name only as Alla welcomed the prospects of a new beginning as life had been hard in the Ukrainian town of Yenakievo, where she worked for a coal mining company. She has a job offer but was holding out for a better one.
She said people in Yenakievo were tired of "living like beggars" and sending taxes to Ukraine's national government in Kiev: "All the money was going to Kiev and we were just getting the leftovers."
Employers in Belgorod include a facility that calibrates meters for the oil and gas industry. The new plant, the only one of its kind in Russia, is willing to employ qualified refugees.
"We have already hired one Ukrainian. If they have relevant qualifications, we will gladly hire them," Sergei Samsonov, the head of the facility, said.
For now refugees seem able to pick and choose, but some lawmakers have proposed cutting their benefits if they turn down three job offers.
The refugees are gradually replacing some of the migrant workers abundant in Russian cities long before the conflict began, many from former Soviet republics in Central Asia and willing do the menial jobs Russians dislike and for lower wages.
"Forced migration from Ukraine ... will soon transform into labour and economic migration," Konstantin Romodanovsky, head of Russia's Federal Migration Service, said in a recent radio interview.
This is a welcome development for the government as Russia is in need of migrants to plug the gaps in a workforce declining as the average age of the population grows and to help the economy, suffering from the impact of Western sanctions imposed over the crisis in Ukraine.
Romadanovsky said the Russian government had allocated 6 billion roubles for the refugees in addition to financial assistance from local funds.
Not everyone in Belgorod is happy at the generosity offered to the refugees.
Alexei, a university student who works part-time at a local cafe that provides free meals to refugees, says he believes most of them are content living off state handouts.
"They (the refugees) got 150 free places at university while we, the locals, have to work late hours to pay for our tuition," he said.
Another Belgorod resident, Alena, said: "Just imagine, we bring children's clothes (to aid distribution points) and instead of a 'thank you' they demand a children's bike."
Eight-year-old Bogdan Divenko senses the resentment, saying he is treated differently to Russian children at school. But he is happy to be safe and dreams of a getting Russian citizenship.
"When am I going to become a Russian citizen? I'm tired of them not even using my name at school. For them, I'm just a refugee," his mother quoted him as saying.












Add new comment